Archiwum dla miesiąca: December 2017
FMEA analysis in hospital
Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) in hospital
Every day while working in a hospital, a doctor’s office or laboratory there may occur situations that can cause errors and generate costs. Sometimes these are necessary activities related to the provision of a medical service, sometimes these are activities that could be avoided. These activities may be related to mistakes and errors that are not detected at an early stage of creation can bring huge losses to the organization. Not only financial but also reputational losses. Analyzing the operating costs of medical institution, they can be divided into fixed and variable costs.
Fixed costs usually remain at a comparable level, while variable costs depend not only on the number of patients who use the hospital services each year but also on the number and complexity of processes, i.e. services offered by the medical institution. Each hospital ward, clinic, laboratory consists of main and auxiliary processes. Each process consists of activities in which there are potential risks. Each risk is a potential cost for the company and additional work.
Risk management
Failure mode and effects analysis FMEA is not only an additional way to solve problems but also a way to meet the new requirements of the Quality Management System according to ISO 9001: 2015. Risk management is a set of activities that are aimed at controlling the risk. Clinical risk is the combination of the probability of an event and its consequences, which will have a negative impact on the outcome of the patient treatment. There are many methods of risk management and what will be chosen depends not only on the decisions of main management but also on:
- The number of processes occurring in the organization
- Complexity of processes and level of maturity
- Employees awareness of processes
- Accessibility of resources, i.e.: working time of medical and non-medical personnel, available conference room
- Employees knowledge of risk analysis
The methods of risk estimation, most often used, are presented below:
- FMEA method- failure mode and effects analysis- The FMEA analysis is divided into:
- SFMEA- FMEA for the management system
- PFMEA- FMEA for the clinical process
- DFMEA- FMEA for design, construction of medical equipment
- MFMEA- FMEA for machinery, medical equipment
- SAC analysis
- Strategic management
The goals of using the FMEA in a medical institution:
- Identification of the causes of errors
- Documenting the process
- Permanent elimination of errors in the process and critical places / activities that may be a “weak link”
- Continuous improvement of the process through the introduction of amendments and new solutions depending on the level of risk
- Creating a knowledge base on the most important processes in the organization and activities related to them, such as preventive, corrective and improving actions
A detailed analysis should be made to estimate the risk. The following stages are presented below:
- Collect the applicable procedures and instructions in the process.
- These can be procedures such as hospitalization in a ward.
- Gather process participants – create a team for risk analysis.
2.2. The team should be multidisciplinary, consisting of several different specialists related to the process as well as people who don’t work directly in the process. The team should consist of 3 to 5 people, with specializations such as doctor, nurse, technician, ward nurse or registrant. An analysis leader should be selected that will document risk estimation and organize meetings.
- Create a flowchart – a graphical diagram which shows the course of the process from the moment of requesting the service until the patient leaves the medical institution.
3.3. If such flowcharts do not exist, they can be created with the team, specifying the decision-making places, people responsible for performing the activities and the necessary medical documentation needed to perform the service. The diagram will be the basis for the analysis of individual activities. The more extensive it is, the longer the analysis will take, while it will be more detailed and the later plan will be more likely.
- Collect a register of non-conformities, adverse events, medical incidents and other if they exist.
- Collect a register of comments from patients and other interested parties.
- Collect the results of the satisfaction surveys of patients, employees and other interested parties.
- Analyze each activity for potential errors that may occur during its implementation. It is best to brainstorm for potential mistakes and collect historical data from the registers.
FMEA analysis is different from the others because it is very detailed and work-intensive. It depends on the team how the process will be analyzed and whether all information will be taken into account. The analysis should be objective and true. The analysis determines three factors on the basis of which the product is calculated which shows the level of risk. These are:
- The significance of the error for the patient
- Frequency of the defect
- The method of detecting the defect
The rating scale is from 1 to 10, with 1 being the least negative impact while 10 means the highest negative impact. The scale is universal and is used throughout the world by various industries.
- Next stage is to define the significance of the defect for the patient / client.
- The next stage is to determine the cause of the error – potential risk. There can be many reasons for any potential error. To collect them and sort thematically, dedicated tools can be used.
Only after collecting information about the process, knowing the sequence of individual activities and critical places in the process, which are particularly important and influence the result of the process, it is possible to undertake the analysis of potential risks. Potential causes of errors can be collected by usage of tools such as:
- 5WHY
- ISHIKAWA diagram – fishbone
- brainstorm (1×1, 6x3x5, 6×6 Philips)
- Knowing the potential causes of errors, the frequency of occurrence should be assessed. Participants should be asked how often the error may occur or occurred in the past. Is it once a day, a week, a year? Maybe the medical institution has statistics on recurring adverse events or other errors?
- Next stage is to specify how to detect the error. To what extent the process participants are able to notice an error during their daily work. If it is instant, using sensors and light and sound signals it’s good. If it is not possible to detect the error, this must also be included in the analysis. The methods of process supervision and error detection include such solutions as poka-yoke, jidoka, system Andon, visual management. You can find more information in lean Techniques.
- The next stage is to assess the detection of errors.
- With a specific risk factor, it is possible to calculate the RPN (Risk Priority Number). The rating range is from 1 to 1000. The higher the number, the higher the probability of risk.
The result of the RPN indicates for which risks improvement and prevention actions should be taken and which can be accepted without taking major measures. The universal scale indicates that for risks above 100 points, actions should always be taken. Such a risk is defined as critical and is probably a threat to the participants of the process, the indicated errors can be expected in the near future. The risk in the 60-100 range is high and taking action depends on the organization and decisions of not only the team but also the main management. Actions may be implemented but not mandatory. For risks below 60 points it is not needed to take action, as it is usually an acceptable level of risk. You can find more about risk management in the next article.
- Risk estimation and the RPN result is not the last stage in the analysis. The result indicates for which activities the actions should be taken. It should be remembered that the significance of the error for the patient can’t be reduced, it is possible to implement actions reducing the level of error or its detection. It all depends on the organization’s capabilities, resources, the maturity of the process and the involvement of co-workers.
- After defining the preventive actions , plan of action should be defined, which indicates how to reduce the frequency of errors and how to detect them. The action plan consists of a task, a responsible person and a deadline for implementation.
- After the action is performed, the error and the method of detection should be estimated again. The new RPN score should be lower than the original one. This will be evidence of effective actions and good risk management in clinical processes.
How to maintain the implemented changes and reduce the level of potential risks? The PCP-PROCESS CONTROL PLAN, which is created on the basis of the FMEA analysis will help us.. The plan allows for continuous monitoring of the process and the implementation of any post-audit actions. Remember that every change in the process carries with it new, potential risks that can change the action plan. For each time the order of action in the process changes, new medical equipment arrive, the place of health care implementation changes, the FMEA analysis should be reviewed and updated.
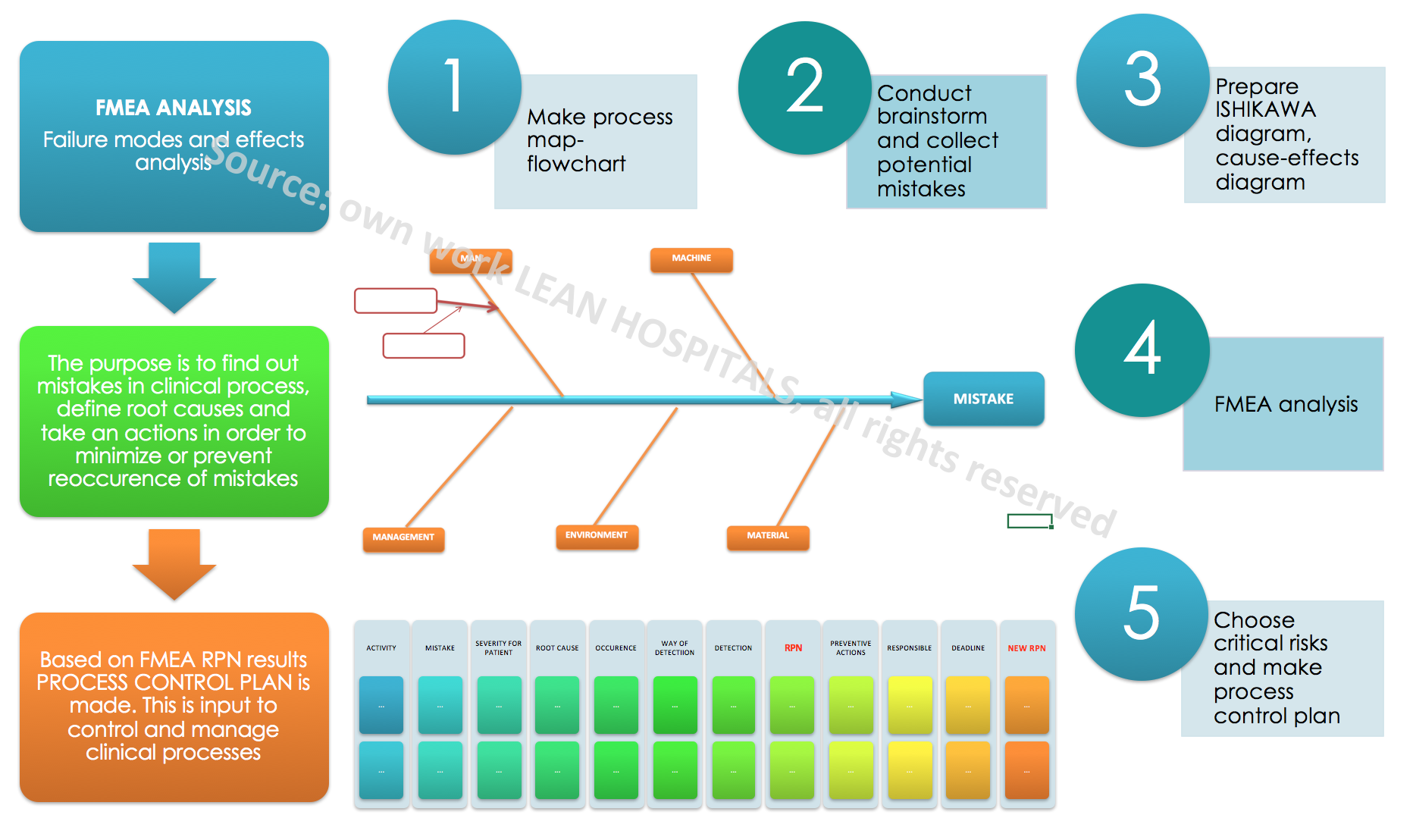
It should be remembered that without having many detailed data on risk, it isn’t possible to assess but only to estimate its level. Estimation is related to the opinion of a multidisciplinary team, which is able to determine the potential risk based on their own experience. Advantages of the method:
- Detailed knowledge of clinical processes
- Increased awareness of employees, in particular medical personnel, about the causes of errors
- Increased process cycle efficiency – PCE
- Improved patient safety
- Increased customer satisfaction
- Improved communication in the hospital because of teamwork
- Reduced costs of organization activities
Disadvantages of the method:
- The need for knowledge of extended tool
- The procedure is time-consuming
Practical experience shows that a well-made FMEA analysis allows to implement processes without any errors or mistakes. Such a positive result is achieved due to the consequences of the action and compliance with the procedures. The system created by everyone, both employees and customers.
Lean accounting in hospital
Effective methods of cost management in a medical institution using lean accounting.
Running a business involves great responsibility and responsibilities. Both the knowledge of legal requirements and expectations of other interested parties and the most important clients, have great importance in the success of the project. The type of industry in which the company operates and financial management are factors that affect the level of expenses and profits of the organization. The goal of every financial management company is to get and use the right amount of funds to increase the value of the company. The measure of efficiency and business proficiency is profitability. Profitability is defined as a higher level of revenues over expenses. In order to gain a competitive advantage, an institution should achieve better economic results by choosing appropriate methods of cost management.
One of the discussed methods will be the ABC – Activity Based Costing method. The ABC method activity costs account allows you to accurately determine indirect costs, which fall on the offered service and product. According to this method, indirect costs are billed to products. Due to the large number of processes that occur in the company, they lead to the creation of a product at the exit of the process.
The stages of the ABC method are based on four basic steps:
- Defining resources
- Identification of activities
- Defining the costs of activities
- Settlement of the costs of activities on products
Assumptions on which the ABC method is based relate to:
- Costs that express expenses incurred to obtain materials and resources for the organization’s services (input data to processes)
- Various activities which can lead to the consumption of the same resources
- Actions that are expressed in the appropriate unit
- The costs are settled in the chapter for individual products or services. Another method of financial management that could be the most effective for the described company is time-driven ABC which is a time-controlled cost account. Improper management, including time, ineffective communication, problems with service providers (delivery of lunches, external service of washing bedlinen) and technical errors that may affect the economic results. It is important to look for solutions that will eliminate bottlenecks and will streamline hospital processes which will improve its profitability. The TDABC method allows company to adjust the cost account to seasonality and above all, uneven demand for services provided by the organization. Both methods require from management of clinical processes a process approach, which includes all main and auxiliary processes as well as their interrelationships and resources as well as output data (SIPOC). The method requires horizontal management by main management.
In the discussed case, two methods of cost management for a medical institution will be presented. Each hospital, clinic, doctor’s office are entities that provide medical services. The main purpose of the activity is to provide medical services. Depending on the business profile, the main process may be a clinical process, e.g. basic health care, hemodialysis process and outpatient specialist care. On the implementation of health services consist, depending on the expectations and needs of the patient, such sub-processes as:
- analysis of the requirements of the payer and other interested parties
- designing of clinical processes
- registration of patients
- implementation of medical advices
- implementation of specialist advices
- wykonanie diagnostyki laboratoryjnej
- management of medicine administration
- training of medical staff and other specialists
- solving problems occurring in processes
- implementation of the proposed solutions, e.g. 5S- orderly workplace, ANDON, visual management
- monitoring results of processes and implementing improvement actions
Part of the processes depends not only on the profile of the medical institution (whether it is a public, multi-specialized hospital, private medical center, clinic, laboratory, other private unit providing for example magnetic resonance services), also depends on size and structure (e.g. number of hospital departments, complexity of hospitalization processes and procedures, type of management – silo or horizontal, process awareness and quality management systems). Another factor influencing the scope of services is the impact of the main management approach to the knowledge of the lean healthcare method and the awareness of the occurrence of problems and the level of process maturity. The higher the level of maturity, the more criteria and information on the basis of which the process can be controlled and planned. The implementation of lean healthcare projects may concern:
- Implementation of a quality management system in a multi-specialist public hospital with lean tools to analyze clinical risks
- process optimization in a specialist hospital (Kanban cards, 5S, visual management, FMEA risk management, 5why problem solving, A3)
- design of the laboratory space for more efficient work with usage of the spaghetti diagram and other lean healthcare tools
- conducting training for the medical staff on the topics of: communication with a difficult patient, keeping medical records, solving problems using the Ishikawa diagram, A3, 8D, 5why
Referring to the processes occurring in a medical institution, it can generate costs due to:
- Reporting demands of patients for non-standard services because each medical service is unique
- Occurrence of downtime and other waste (8 types of muda)
- Inefficient use of machinery and medical equipment
- Occurrence of errors: medical incidents, adverse events, complaints, reoperations
Based on the ABC, it is very easy to identify activities that exist in the organization.
For example, it is possible to analyze the patient’s treatment process. Table 1 shows the path of the patient from registration to discharged from the hospital ward.
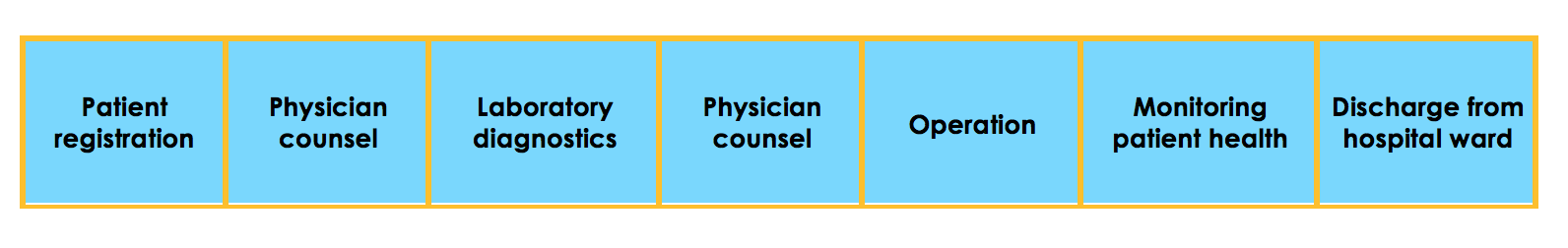
Table 1, Identified actions, source: own work
After identifying the activities, it is possible to determine the volume measurement unit of each measure. The proposals are presented in the table No. 2.

Table 2, Identified measures for actions, source: own work
The next step is to determine the costs of activities. They are determined individually. There also occur variables such as:
- Type of provided service
- The number of repetitions of a service
- Type of specialist doctor
- The type of medical equipment needed for survey (Ultrasound, artificial kidney, catheter)
- Estimated time to provide the service
- Effectiveness of the performed procedure
The estimated costs of each activity for the medical service delivery process are listed below. It consists of both variable and fixed costs. Fixed costs are:
- maintenance of the hospital infrastructure
- salaries for employees of the institution
- depreciation of fixed assets
Variable costs apply to those activities that can be performed repeatedly, such as:
- medical consultation
- performing a diagnostic survey
- the amount of used disposable equipment
- usage of medicines
Each patient is unique, therefore the medical service is adapted to the type of process. (e.g. performing operations on the operating block), number of participants (doctors, nurses, instrumenter, ward nurse, duration of the process (non-invasive surgery – 3h, invasive surgery-7h).
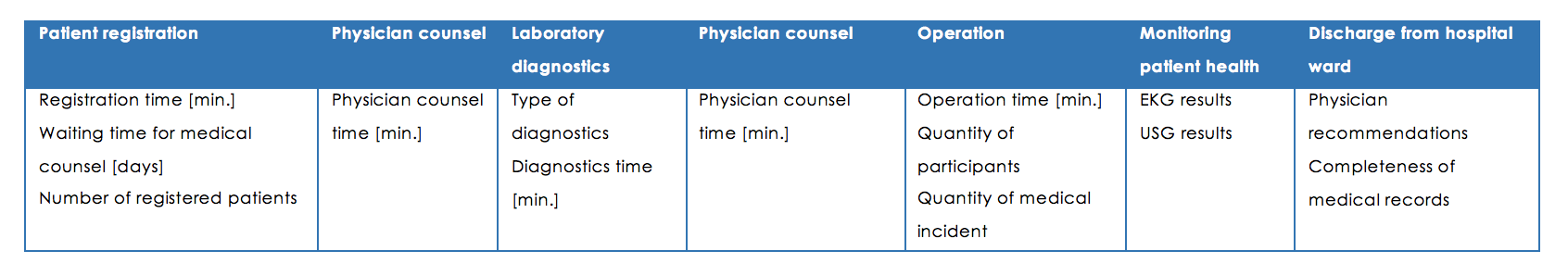
Table 3, Data for costs of actions, source: own work
The last activity is the settlement of the costs of activities for particular services / treatments. Thanks to the process approach, it is possible to optimize the activities occurring in it, which may affect the costs of the process. The ABC method allows to customize the service that is offered by medical institutions to patients in a specific chapter on activities. Because of having information about the costs of the operation, the hospital or other medical entity has the possibility of real valuation of the service and offering a flexible offer to clients. Another method that will allow to effectively manage available resources, mostly human resources and time is the Time Driven ABC method. In order to apply this innovative method, the main and auxiliary processes and their structure should be very well known. Each activity is closely related to the work of a individual person. Due to the complexity of the processes occurring in the hospital, their number and interrelationships, the employee’s time intended to the activities presented in Table 1 is different. At the beginning of the medical service, the time can be estimated.
In order to analyze business processes, service processes must be documented in detail and a set of skills necessary for their implementation must be specified. A tool that will help in understanding the process is VSM-value stream mapping, which indicate activities that add value in the process and bottlenecks. It is a detailed analysis of activities, their sequence and time of performing particular activities. Map of the value stream mapping for the operation process in the orthopedics ward is described below. Obtaining such a map by the hospital allows not only to evaluate each activity, but also to assess the duration of activity. The map indicates inefficient places (both in terms of waste of time and financial resources). In order to achieve lower costs of services, it would be necessary to eliminate these activities (orange marked), which generate unnecessary costs.
On the basis of detailed knowledge of service processes, it is possible to define the time frame necessary for the implementation of activities and then the costs of their implementation.
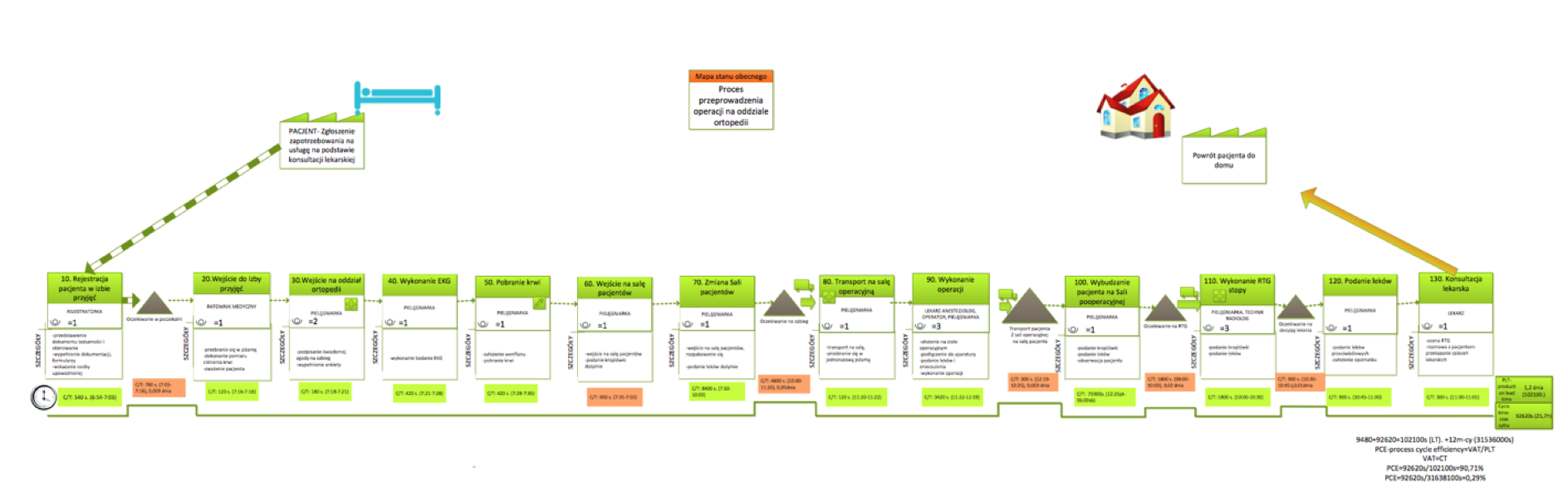
Diagram nr 1, Current state map, source: own work
Based on the information contained in Diagram 1 it is possible to:
- Forecast the use of human resources, time resources and others.
- Correct and improve the procedures for the implementation of individual services, e.g. the procedure of patient catheter placement
- Reduce the costs of implementing individual activities – e.g. surgical treatment
- Adjust the number of personnel and their time to specific medical services, e.g. number of medical caregivers in a ward
- Monitor the process of provided services and if necessary, supplement them with missing resources (e.g. additional doctor or additional time for the implementation of the action).
- Eliminate risks, relying on agile service delivery and respond In right time
- Use the kaizen costing method, which strives to reduce the costs of service delivery because of continuous process optimization.
The TD ABC method is an opportunity for every medical institution, because of the ability to manage variable costs. Based on adjusting the time of work of medical staff to the needs of the client / patient, the company can achieve profits proportional to the used resources (working time of the medical staff, used medicaments, disposable materials). It is a method for business risk management, e.g. potential risk – lack of possibility to perform laparoscopy due to the shortage of disposable materials and medicines.
The type of activity of each medical institution allows to cost management through ABC and time driven ABC methods, which are a chance to improving the company’s operations and increasing financial efficiency. This choice increases the possibilities of gaining a competitive advantage. A detailed elaboration of the costs of the implementation of the main processes, including the necessary time for implementation, will allow to secure the services and their continuity, without the risk that the company has unqualified specialists, lack of needed staff or lack tools to perform the treatment.
Footnotes
Books
- Janusz Janczarski, MBA BCC 15, Financial accounting 09-11.06.2017, GFKM.
Internet sources
- https://mfiles.pl/pl/index.php/Rachunek_kosztów_działań, z dnia 10.10.2017, Encyclopedia website
- http://www.pracownicy.ue.poznan.pl/masztalerz/zrz.wyk.01.pdf z dnia 10.10.2017, University of Economics in Poznan
- http://procesy.ue.wroc.pl/index.php/materialy-dla-studentow/zarzadzanie-procesami/abc—rachunek-procesowy-kosztow.html z dnia 10.10.2017, University of Economics in Wroclaw
- http://www.egospodarka.pl/33953,Rachunek-kosztow-TDABC-metodyka-wdrazania,1,20,2.html z dnia 10.10.2017, Website for entrepreneurs
